1. 简介 Mycat 是一个彻底开源的新颖的数据库中间件产品,它接受客户端SQL请求,根据路由分片发送至后端数据库集群,然后返回响应数据给客户端。它有效解决了传统数据库的瓶颈问题,从而使数据库的高可用,高负载成为可能。那么它的内部是怎么实现的呢?本文我们就Mycat源码分析研究一下后端连接处理的实现方式与内部机制,这里抛砖引玉,希望与感兴趣的朋友共同交流探讨。https://github.com/MyCATApache/Mycat-Server/tree/1.6/src/main/java/io/mycat
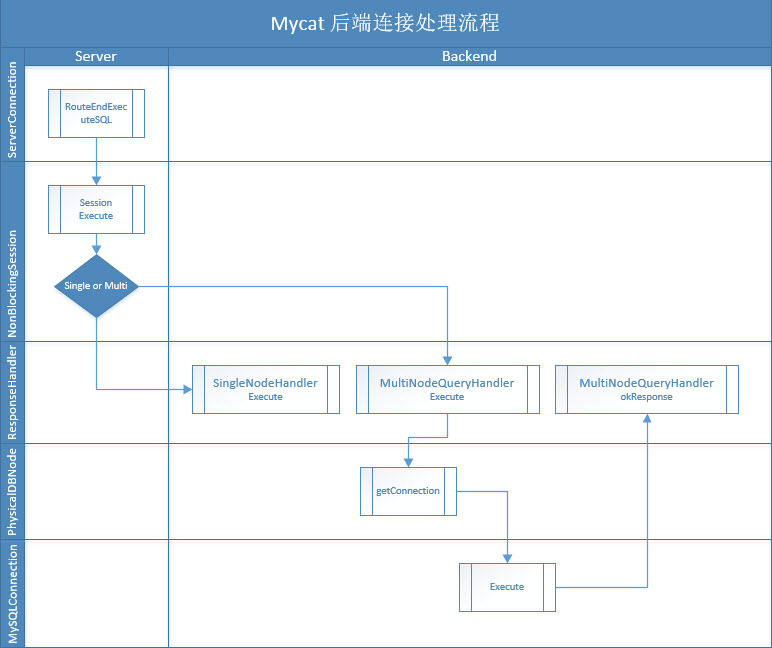
2. 流程图 后端连接处理流程主要指mycat server接收到路由以后下发SQL语句至具体的datahost执行并返回报文的一段过程。以下是主要流程图。
3. routeEndExecuteSQL 类ServerConnection包含routeEndExecuteSQL方法,路由计算成功,去调用类NonBlockingSession的execute方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public void routeEndExecuteSQL (String sql, int type, SchemaConfig schema) RouteResultset rrs = null ; try { rrs = MycatServer .getInstance() .getRouterservice() .route(MycatServer.getInstance().getConfig().getSystem(), schema, type, sql, this .charset, this ); } catch (Exception e) { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); LOGGER.warn(s.append(this ).append(sql).toString() + " err:" + e.toString(),e); String msg = e.getMessage(); writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ER_PARSE_ERROR, msg == null ? e.getClass().getSimpleName() : msg); return ; } if (rrs != null ) { session.execute(rrs, type); } }
4. 类NonBlockingSession的execute方法 类NonBlockingSession的execute方法对路由结果做了判断,如果不存在任何需要派发的节点则直接返回,如果是单节点,则调用类singleNodeHandler方法execute,如果是多节点,则调用类MultiNodeQueryHandler方法execute。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public void execute (RouteResultset rrs, int type) clearHandlesResources(); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); LOGGER.debug(s.append(source).append(rrs).toString() + " rrs " ); } RouteResultsetNode[] nodes = rrs.getNodes(); if (nodes == null || nodes.length == 0 || nodes[0 ].getName() == null || nodes[0 ].getName().equals("" )) { source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ER_NO_DB_ERROR, "No dataNode found ,please check tables defined in schema:" + source.getSchema()); return ; } if (nodes.length == 1 ) { singleNodeHandler = new SingleNodeHandler(rrs, this ); if ( this .isPrepared() ) { singleNodeHandler.setPrepared(true ); } try { singleNodeHandler.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.warn(new StringBuilder().append(source).append(rrs).toString(), e); source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ERR_HANDLE_DATA, e.toString()); } } else { boolean autocommit = source.isAutocommit(); multiNodeHandler = new MultiNodeQueryHandler(type, rrs, autocommit, this ); if (this .isPrepared()) { multiNodeHandler.setPrepared(true ); } try { multiNodeHandler.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.warn(new StringBuilder().append(source).append(rrs).toString(), e); source.writeErrMessage(ErrorCode.ERR_HANDLE_DATA, e.toString()); } } if (this .isPrepared()) { this .setPrepared(false ); } }
5. 类MultiNodeQueryHandler的execute方法 单节点与多节点的原理是一样的,只是多节点多了一层循环,对每个datanode分别进行了同样的操作。这里先判断session是否已经有该datanode关联的后端连接session.tryExistsCon,如果已有,则调用_execute方法下发SQL指令;反之,则调用getConnection方法从连接池中获取一个可用连接或新建一个连接。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public void execute () throws Exception final ReentrantLock lock = this .lock; lock.lock(); try { this .reset(rrs.getNodes().length); this .fieldsReturned = false ; this .affectedRows = 0L ; this .insertId = 0L ; } finally { lock.unlock(); } MycatConfig conf = MycatServer.getInstance().getConfig(); startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); LOGGER.debug("rrs.getRunOnSlave()-" + rrs.getRunOnSlave()); for (final RouteResultsetNode node : rrs.getNodes()) { BackendConnection conn = session.getTarget(node); if (session.tryExistsCon(conn, node)) { LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()-" + node.getRunOnSlave()); node.setRunOnSlave(rrs.getRunOnSlave()); LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()-" + node.getRunOnSlave()); _execute(conn, node); } else { LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()1-" + node.getRunOnSlave()); node.setRunOnSlave(rrs.getRunOnSlave()); LOGGER.debug("node.getRunOnSlave()2-" + node.getRunOnSlave()); PhysicalDBNode dn = conf.getDataNodes().get(node.getName()); dn.getConnection(dn.getDatabase(), autocommit, node, this , node); } } }
6. 类MySQLConnection的execute方法 这里execute方法判断是否已执行,同时同步并执行synAndDoExecute方法,最后调用底层命令sendQueryCmd。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 public void execute (RouteResultsetNode rrn, ServerConnection sc, boolean autocommit) throws UnsupportedEncodingException if (!modifiedSQLExecuted && rrn.isModifySQL()) { modifiedSQLExecuted = true ; } String xaTXID = sc.getSession2().getXaTXID(); synAndDoExecute(xaTXID, rrn, sc.getCharsetIndex(), sc.getTxIsolation(), autocommit); } private void synAndDoExecute (String xaTxID, RouteResultsetNode rrn, int clientCharSetIndex, int clientTxIsoLation, boolean clientAutoCommit) String xaCmd = null ; boolean conAutoComit = this .autocommit; String conSchema = this .schema; boolean expectAutocommit = !modifiedSQLExecuted || isFromSlaveDB() || clientAutoCommit; if (expectAutocommit == false && xaTxID != null && xaStatus == 0 ) { clientTxIsoLation = Isolations.SERIALIZABLE; xaCmd = "XA START " + xaTxID + ';' ; } int schemaSyn = conSchema.equals(oldSchema) ? 0 : 1 ; int charsetSyn = 0 ; if (this .charsetIndex != clientCharSetIndex) { setCharset(CharsetUtil.getCharset(clientCharSetIndex)); charsetSyn = 1 ; } int txIsoLationSyn = (txIsolation == clientTxIsoLation) ? 0 : 1 ; int autoCommitSyn = (conAutoComit == expectAutocommit) ? 0 : 1 ; int synCount = schemaSyn + charsetSyn + txIsoLationSyn + autoCommitSyn; if (synCount == 0 ) { sendQueryCmd(rrn.getStatement()); return ; } CommandPacket schemaCmd = null ; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); if (schemaSyn == 1 ) { schemaCmd = getChangeSchemaCommand(conSchema); } if (charsetSyn == 1 ) { getCharsetCommand(sb, clientCharSetIndex); } if (txIsoLationSyn == 1 ) { getTxIsolationCommand(sb, clientTxIsoLation); } if (autoCommitSyn == 1 ) { getAutocommitCommand(sb, expectAutocommit); } if (xaCmd != null ) { sb.append(xaCmd); } if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("con need syn ,total syn cmd " + synCount + " commands " + sb.toString() + "schema change:" + (schemaCmd != null ) + " con:" + this ); } metaDataSyned = false ; statusSync = new StatusSync(xaCmd != null , conSchema, clientCharSetIndex, clientTxIsoLation, expectAutocommit, synCount); if (schemaCmd != null ) { schemaCmd.write(this ); } sb.append(rrn.getStatement()); this .sendQueryCmd(sb.toString()); }
7. 类MultiNodeQueryHandler的okResponse方法 在类MySQLConnection的execute方法执行前,其实我们已经通过conn.setResponseHandler(this)将接收返回的数据报文。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 public void okResponse (byte [] data, BackendConnection conn) this .netOutBytes += data.length; boolean executeResponse = conn.syncAndExcute(); if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("received ok response ,executeResponse:" + executeResponse + " from " + conn); } if (executeResponse) { ServerConnection source = session.getSource(); OkPacket ok = new OkPacket(); ok.read(data); boolean isCanClose2Client =(!rrs.isCallStatement()) ||(rrs.isCallStatement() &&!rrs.getProcedure().isResultSimpleValue());; if (!isCallProcedure) { if (clearIfSessionClosed(session)) { return ; } else if (canClose(conn, false )) { return ; } } lock.lock(); try { if (!rrs.isGlobalTable()) { affectedRows += ok.affectedRows; } else { affectedRows = ok.affectedRows; } if (ok.insertId > 0 ) { insertId = (insertId == 0 ) ? ok.insertId : Math.min( insertId, ok.insertId); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } boolean isEndPacket = isCallProcedure ? decrementOkCountBy(1 ) : decrementCountBy(1 ); if (isEndPacket&&isCanClose2Client) { if (this .autocommit) { session.releaseConnections(false ); } if (this .isFail() || session.closed()) { tryErrorFinished(true ); return ; } lock.lock(); try { if (rrs.isLoadData()) { byte lastPackId = source.getLoadDataInfileHandler() .getLastPackId(); ok.packetId = ++lastPackId; ok.message = ("Records: " + affectedRows + " Deleted: 0 Skipped: 0 Warnings: 0" ) .getBytes(); source.getLoadDataInfileHandler().clear(); } else { ok.packetId = ++packetId; } ok.affectedRows = affectedRows; ok.serverStatus = source.isAutocommit() ? 2 : 1 ; if (insertId > 0 ) { ok.insertId = insertId; source.setLastInsertId(insertId); } ok.write(source); } catch (Exception e) { handleDataProcessException(e); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } }
小结,对比1.5正式版本,1.6版本重构了包名,框架看上去更加清晰。我这里只是粗略的对后端连接处理做了分解,肯定有错误之处,还望谅解。