1. 简介
为了更好的实现负载均衡和消息的顺序性,Kafka Producer可以通过分发策略发送给指定的Partition。Kafka保证在partition中的消息是有序的。
- 一个Partition只分布于一个Broker上(不考虑备份)
- 一个Partition物理上对应一个文件夹
- 一个Partition包含多个Segment(Segment对用户透明)
- 一个Segment对应一个文件
- Segment由一个个不可变记录组成
- 记录只会被append到Segment中,不会被单独删除或者修改
- 清除过期日志时,直接删除一个或多个Segment。
消息被路由到哪个partition上,是有producer客户端决定的.比如客户端采用random,hash及RoundRobin轮询等,如果一个topic中有多个partitions,那么在producer端实现”消息均衡分发”是必要的,producer通过设置partitioner.class的属性来指定向那个分区发送数据。
下面我们就实际演示Producer的分发策略。
2. 准备工作
2.1 启动zookeeper,kafka
sudo docker start zookeeper
sudo docker start kafka`</pre>
Docker设置方法参见上文。
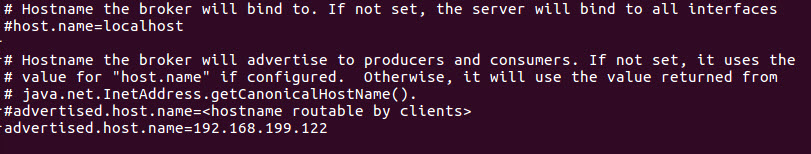
2.2 参数修改
将kafka docker中的server.properties配置文件的advertised.host.name改成docker宿主机的IP地址,以便远程客户端访问。
advertised.host.name=192.168.199.122
3. 启动Eclipse(本地windows端)
3.1 新建project
新建一个maven project(Eclipse 安装设置方法参见本博其他文章)。
编辑pom.xml 在下加入以下代码
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka_2.11</artifactId>
<version>0.8.2.2</version>
</dependency>
保存后,eclipse自动获取kafka相关jar文件。
3.2 DemoConsumer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import kafka.consumer.Consumer;
import kafka.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import kafka.consumer.ConsumerIterator;
import kafka.consumer.KafkaStream;
import kafka.javaapi.consumer.ConsumerConnector;
import kafka.message.MessageAndMetadata;
public class DemoConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
args = new String[]{"192.168.199.122:2181", "topic1", "group1", "consumer1"};
if (args == null || args.length != 4) {
System.err.print(
"Usage:\n\tjava -jar kafka_consumer.jar ${zookeeper_list} ${topic_name} ${group_name} ${consumer_id}");
System.exit(1);
}
String zk = args[0];
String topic = args[1];
String groupid = args[2];
String consumerid = args[3];
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("zookeeper.connect", zk);
props.put("group.id", groupid);
props.put("autooffset.reset", "largest");
props.put("autocommit.enable", "true");
props.put("client.id", "test");
props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");
ConsumerConfig consumerConfig = new ConsumerConfig(props);
ConsumerConnector consumerConnector = Consumer.createJavaConsumerConnector(consumerConfig);
Map topicCountMap = new HashMap();
topicCountMap.put(topic, 1);
Map<String, List<KafkaStream>> consumerMap =
consumerConnector.createMessageStreams(topicCountMap);
KafkaStream stream1 = consumerMap.get(topic).get(0);
ConsumerIterator it1 = stream1.iterator();
while (it1.hasNext()) {
MessageAndMetadata messageAndMetadata = it1.next();
String message =
String.format("Consumer ID:%s, Topic:%s, GroupID:%s, PartitionID:%s, Offset:%s, Message Key:%s, Message Payload: %s",
consumerid,
messageAndMetadata.topic(), groupid, messageAndMetadata.partition(),
messageAndMetadata.offset(), new String(messageAndMetadata.key()),new String(messageAndMetadata.message()));
System.out.println(message);
}
}
}
|
3.3 ProducerDemo
使用RandomPartitioner.class.getName()确保每个producer实例使用单独Partitioner实例。下面的例子使用了两个producer实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
import kafka.javaapi.producer.Producer;
import kafka.producer.KeyedMessage;
import kafka.producer.ProducerConfig;
import kafka.serializer.StringEncoder;
public class ProducerDemo {
static private final String TOPIC = "topic1";
static private final String ZOOKEEPER = "192.168.199.122:2181";
static private final String BROKER_LIST = "192.168.199.122:9092";
static private final int PARTITIONS = 3;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String pt = "RoundRobinShare2";
Producer producer = initProducer(pt);
Producer producer1 = initProducer(pt);
sendOne(producer,producer1, TOPIC,pt);
}
private static Producer initProducer(String pt) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("metadata.broker.list", BROKER_LIST);
props.put("serializer.class", StringEncoder.class.getName());
if (pt =="Random" ){
props.put("partitioner.class", RandomPartitioner.class.getName());
}
if (pt =="Hash")
{
props.put("partitioner.class", HashPartitioner.class.getName());
}
if (pt =="RoundRobin")
{
props.put("partitioner.class", RoundRobinPartitioner.class.getName());
}
props.put("producer.type", "sync");
props.put("batch.num.messages", "3");
props.put("queue.buffer.max.ms", "10000000");
props.put("queue.buffering.max.messages", "1000000");
props.put("queue.enqueue.timeout.ms", "20000000");
ProducerConfig config = new ProducerConfig(props);
Producer producer = new Producer(config);
return producer;
}
public static void sendOne(Producer producer,Producer producer1,String topic,String pt) throws InterruptedException {
KeyedMessage message1 = new KeyedMessage(topic, "31", pt + " test 31");
producer.send(message1);
Thread.sleep(5000);
KeyedMessage message2 = new KeyedMessage(topic, "31", pt + " test 32");
producer1.send(message2);
Thread.sleep(5000);
KeyedMessage message3 = new KeyedMessage(topic, "31", pt + " test 33");
producer.send(message3);
Thread.sleep(5000);
KeyedMessage message4 = new KeyedMessage(topic, "31", pt + " test 34");
producer1.send(message4);
Thread.sleep(5000);
KeyedMessage message5 = new KeyedMessage(topic, "31", pt + " test 35");
producer.send(message5);
Thread.sleep(5000);
producer.close();
}
}
|
3.4 Hash策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import kafka.producer.Partitioner;
import kafka.utils.VerifiableProperties;
public class HashPartitioner implements Partitioner {
public HashPartitioner(VerifiableProperties verifiableProperties) {}
public int partition(Object key, int numPartitions) {
if ((key instanceof Integer)) {
return Math.abs(Integer.parseInt(key.toString())) % numPartitions;
}
return Math.abs(key.hashCode() % numPartitions);
}
}
|
我们看到多个producer实例下Key:31会一直发往hash指定的PartitionID:1
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:16, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Hash test 31
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:17, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Hash test 32
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:18, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Hash test 33
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:19, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Hash test 34
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:20, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Hash test 35`</pre>
3.5 Random策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import java.util.Random;
import kafka.producer.Partitioner;
import kafka.utils.VerifiableProperties;
public class RandomPartitioner implements Partitioner {
public RandomPartitioner(VerifiableProperties verifiableProperties) {}
public int partition(Object key, int numPartitions) {
Random random = new Random();
return random.nextInt(numPartitions);
}
}
|
由于是Random策略,Key:31会随机发往Partition
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:21, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Random test 31
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:15, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Random test 32
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:16, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Random test 33
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:17, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Random test 34
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:22, Message Key:31, Message Payload: Random test 35
3.6 RoundRobin策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import kafka.producer.Partitioner;
import kafka.utils.VerifiableProperties;
public class RoundRobinPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private static AtomicLong next = new AtomicLong();
public RoundRobinPartitioner(VerifiableProperties verifiableProperties) {}
public int partition(Object key, int numPartitions) {
long nextIndex = next.incrementAndGet();
return (int)nextIndex % numPartitions;
}
}
|
我们注意到我们使用了AtomicLong来保证多实例共享下线程的安全,关于Atomic的作用,可以参见AtomicInteger在实际项目中的应用。我们看到多个producer实例下Key:31会轮流发往topic1可用的Partition。
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:0, Offset:14, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobin test 31
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:29, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobin test 32
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:21, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobin test 33
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:0, Offset:15, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobin test 34
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:30, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobin test 35`</pre>
4. 验证Partitioner的实例个数及其是否需要保证线程安全
从第2步各种分发策略的实验可知,当指定使用自定义的Partitioner实现后,Producer会使用该实现来作路由决策(即决定消息应该发送到哪个Broker上的哪个Partition)。这就涉及到该类如果是一个实例被共享,需要考虑线程安全的问题,以上我们使用AtomicLong来保证多实例共享下线程的安全。那么如果不使用AtomicLong的情况下,会发生怎样的情况呢?
我们增加一个RoundRobin2策略来演示在共享实例情况下使用和不使用AtomicLong的结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo;
import kafka.producer.Partitioner;
import kafka.utils.VerifiableProperties;
public class RoundRobinPartitioner2 implements Partitioner {
private int i = 0;
public RoundRobinPartitioner2(VerifiableProperties verifiableProperties) {}
public int partition(Object key, int numPartitions) {
long nextIndex = i++;
return (int)nextIndex % numPartitions;
}
}
|
相应的在preducerdemo增加以下代码,RoundRobinShare使用AtomicLong,RoundRobinShare2不使用AtomicLong。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| if (pt =="RoundRobinShare")
{
props.put("partitioner.class", "com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo.RoundRobinPartitioner");
}
if (pt =="RoundRobinShare2")
{
props.put("partitioner.class", "com.alexwu211.kafka.kafa080demo.RoundRobinPartitioner2");
}
|
在使用AtomicLong情况下,轮询正常。
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:61, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare test 31
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:47, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare test 32
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:0, Offset:36, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare test 33
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:62, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare test 34
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:48, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare test 35
在不使用AtomicLong情况下,轮询失败。
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:0, Offset:37, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare2 test 31
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:0, Offset:38, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare2 test 32
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:63, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare2 test 33
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:1, Offset:64, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare2 test 34
Consumer ID:consumer1, Topic:topic1, GroupID:group1, PartitionID:2, Offset:49, Message Key:31, Message Payload: RoundRobinShare2 test 35
结论,由此我们看到实例被共享时,需要一些手段保证线程的安全。
5. 同步异步的参数
上面的例子我们都使用了同步的方法,也就是实时发送,但是如果遇到IO操作等耗时操作时并且不需要让程序等待对方返回,我们可以使用异步发送。异步的好处很明显的,异步可以增加客户体验,可以释放占用资源从而提高系统性能。
kafka中可以使用producer.type参数设置同步还是异步(async/sync),默认是sync。
下面是其它一些相关参数:
- batch.num.messages 异步发送 每次批量发送的条目
- queue.buffering.max.ms 异步发送的时候 发送时间间隔 单位是毫秒
- queue.buffering.max.messages 每次最大的提交量
- queue.enqueue.timeout.ms 0 代表队列没满的时候直接入队,满了立即扔弃,-1代表无条件阻塞且不丢弃


